Billing & Payments Usability Report: Moderated testing how customers interact with Virtual Assistant to complete billing and payment related tasks. View Report >
Georgia Power – Virtual Assistant Customer Service
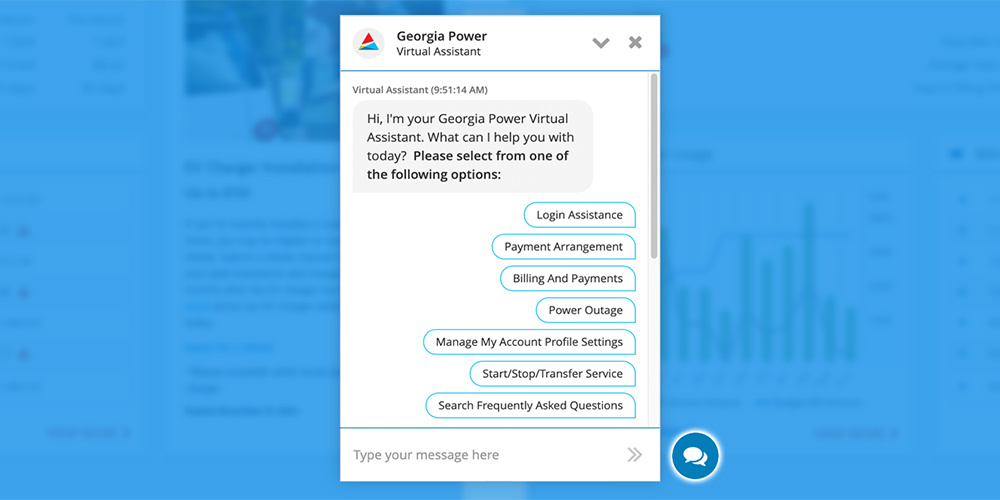
The Georgia Power Virtual Assistant was created to transform utility customer service by providing fast, intuitive, and user-centered support. Through conversational AI, it empowers customers to manage tasks like paying bills, reporting outages, and starting or stopping service—while also reducing operational overhead.
Powered by a large language model (LLM) such as GPT, the assistant uses natural language processing (NLP) to understand user intent and guide conversations. It supports structured workflows through chips, intent recognition, and fallback handling. The model was customized using prompt design, system integrations, and grounding techniques to deliver accurate, policy-aligned responses in a trusted, conversational format.
Client: Georgia Power
Platforms: Web-based Chatbot
Industry: Energy
Role: Lead Product Designer & Manager
Design Team: Myself, UX Designer, UX Researcher
Client Team: Stakeholders, Engineering Team, AI/ML Engineers & SMEs
Time Frame: 3 Months
AI Technical Project Collaboration — Engineering & AI/ML Engineering Teams
Platform Alignment: Collaborated with engineering to understand the capabilities and limitations of the off-the-shelf virtual assistant platform used by Georgia Power.
Task Flow Optimization: Worked closely with engineers to define user journeys, integrate structured task flows (like bill payments and outage reports), and ensure smooth handoffs between assistant and backend systems.
Conversational Flow Design: Partnered with AI/ML engineers to improve how the assistant interpreted intent, handled ambiguous inputs, and guided users through multi-step processes.
Fallback and Escalation Handling: Helped define fallback behavior and escalation triggers to ensure users were supported when the assistant couldn’t resolve an issue.
Language and Tone Consistency: Collaborated on the assistant’s voice, tone, and phrasing to reflect Georgia Power’s brand and provide a clear, trustworthy experience.
Response Accuracy and Guardrails: Advocated for reliable, policy-aligned answers by refining chip labels, intent mapping, and backend logic integration.
Usability Testing and Iteration: Shared insights from user testing to inform assistant behavior updates and improve task clarity, success messaging, and interaction pacing.
Context
Operational and Geographic Context: Serving millions of customers in the southeastern United States, Georgia Power delivers scalable solutions tailored to regional and industry-specific preferences.
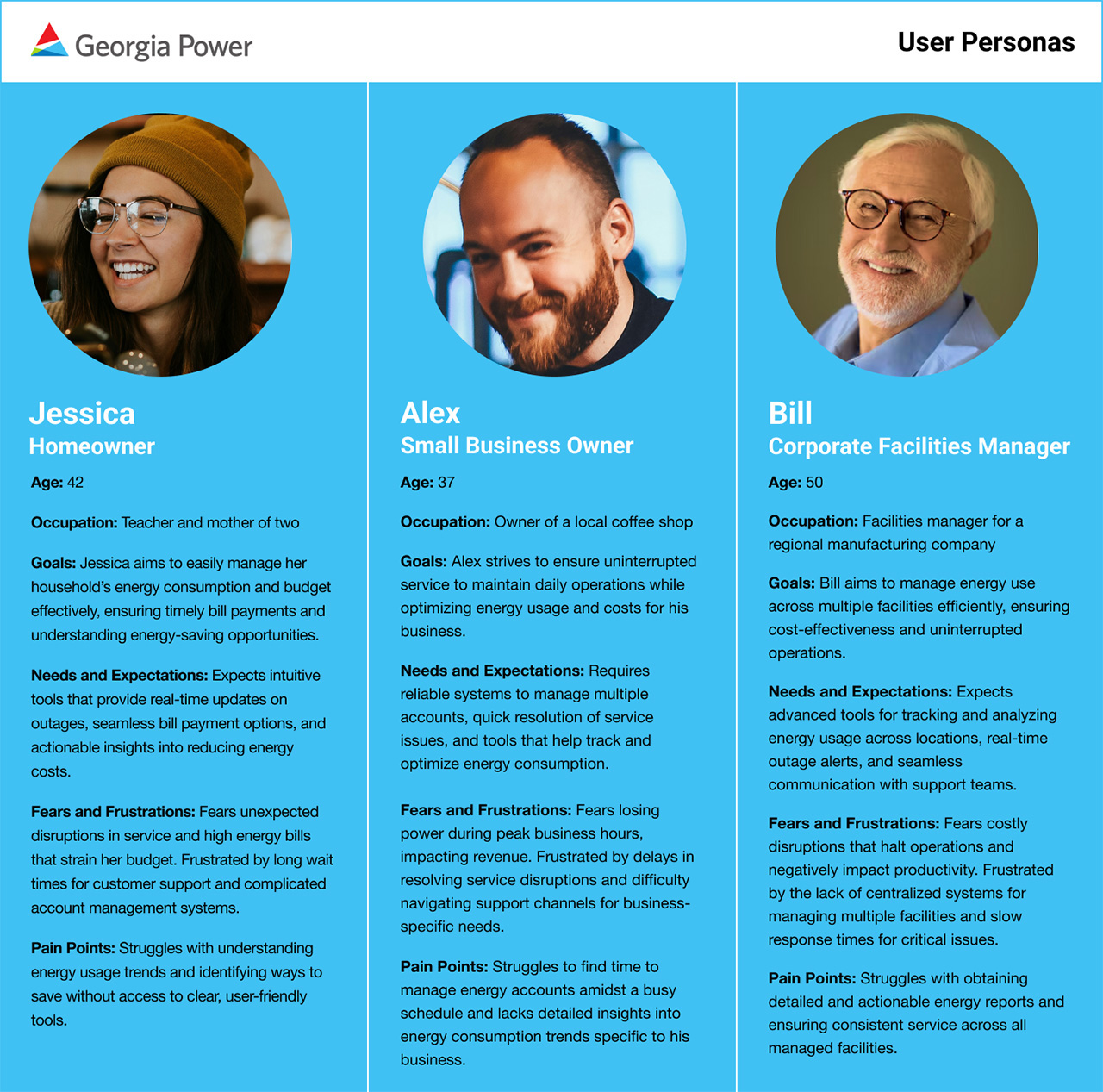
Residential Customers: Homeowners and renters prioritize user-friendly, self-service tools for billing, outages, and energy usage while seeking actionable insights into reducing energy consumption.
Business Customers: Businesses, from small enterprises to large corporations, require systems that effectively manage multiple accounts, ensure uninterrupted service, and provide insights into energy-saving strategies.
Technological Landscape and Platform Vision: Increasing reliance on digital platforms underscores the need for a seamless, multi-device experience that integrates customer feedback and energy industry trends.
Problem
Customer Impact:
-
Dissatisfaction with Support: Long wait times created frustration and reduced customer trust.
-
Complex Processes: Disjointed systems made it difficult for customers to navigate billing, service disruptions, and account updates effectively.
-
Limited Accessibility: A lack of self-service tools, digital literacy barriers, and inconsistent functionality across devices hindered customer independence.
Business Impact:
-
Operational Inefficiencies: Manual workflows and fragmented systems, including data silos, increased costs and slowed response times.
-
Limited Scalability: The existing infrastructure could not handle increasing customer interactions, leading to delays and reduced service quality.
-
Reputation Risks: Inefficient service and unresolved issues eroded customer trust and loyalty, threatening the company’s brand reputation.
Objective
- Enhance Customer Experience: Develop a user-friendly platform to reduce frustration and improve satisfaction through faster, more efficient support.
- Streamline Processes: Simplify workflows for billing, service requests, and account updates, creating a seamless user journey.
- Increase Accessibility: Provide intuitive self-service tools and ensure functionality across all devices, catering to diverse customer needs.
- Improve Operational Efficiency: Automate repetitive tasks, reduce costs, and optimize resource allocation to enhance service quality.
- Strengthen Scalability and Trust: Build a robust infrastructure capable of handling increased interactions while reinforcing customer trust and loyalty through reliable and transparent communication.
UX Process:
Empathize
Tasks:
Reviewed Stakeholder requirements
Conducted interviews with Customers and Stakeholders
Stakeholder Requirements
Key Findings:
- Financial and Operational Impact: Achieve cost savings and streamline workflows through automation while enhancing scalability to accommodate growing demand and optimize resource allocation.
- Enhanced Customer Experience: Improve satisfaction by resolving key pain points like wait times, inconsistent communication, and complex workflows, with an emphasis on real-time updates and trust-building interactions.
- Seamless Integration: Ensure the platform integrates smoothly with existing systems, such as billing, service management, and outage reporting tools, to maintain continuity and reliability.
- Data Security and Compliance: Prioritize robust data protection measures and ensure compliance with industry regulations to safeguard customer information and maintain trust.
- Future-Proofing: Design the platform with flexibility and scalability to adapt to evolving technologies and changing customer needs, ensuring long-term viability.
Interviews
Customers:
Key Pain Points: Customers expressed frustration with long wait times, inconsistent communication, and the lack of intuitive self-service tools for billing and outage updates.
Communication Preferences: A majority of customers preferred digital platforms for support, particularly mobile apps and websites, while emphasizing the need for clear, real-time updates.
Tool Limitations: Current systems were described as outdated and cumbersome, with navigation issues and limited options for resolving queries independently.
Feature Expectations: Customers prioritized features like real-time outage alerts, seamless bill payment options, and detailed energy usage insights to better manage their accounts.
Trust and Transparency: Building trust was crucial, with customers valuing transparent communication about service disruptions and prompt resolutions to their issues.
Stakeholders:
-
Strategic Objectives: Stakeholders highlighted the need to enhance customer satisfaction, reduce operational costs, and improve service scalability.
-
Integration Challenges: Concerns were raised about integrating the platform with existing systems like billing databases and outage reporting tools.
-
Success Metrics: Key performance indicators included reducing customer call volumes, increasing self-service adoption rates, and achieving faster resolution times.
-
Business Alignment: The platform was expected to align with long-term strategies, including the adoption of AI-driven tools and improving data-driven decision-making.
-
Prototyping Insights: Stakeholders emphasized the importance of testing early prototypes with real users to refine functionality and ensure technical feasibility.
I just want a simple way to check my bill, pay it, and get updates if there’s an outage—without having to wait on hold or dig through the website.
Ericka Willby - Georgia Power Customer
Usability Testing
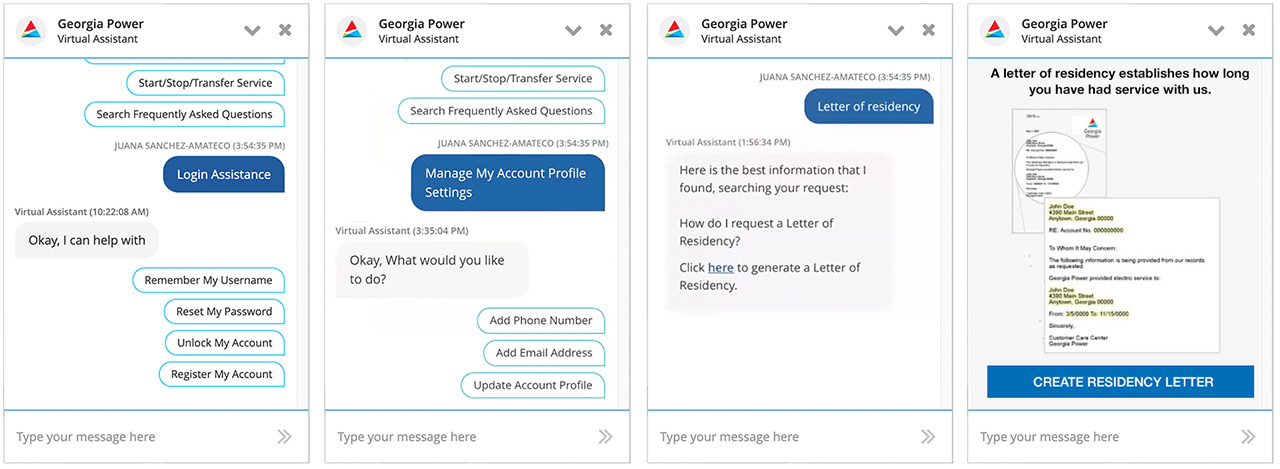
These documents collectively represent a comprehensive series of moderated and unmoderated usability tests conducted on the Georgia Power Virtual Assistant. The studies evaluated how customers interact with the assistant to complete tasks like billing, service orders, payment arrangements, outage reporting, account maintenance, and accessing FAQs. Across different user scenarios, the research uncovered key pain points—such as confusing language, chip label ambiguity, and login-related friction—and provided actionable insights to improve the assistant’s clarity, efficiency, and user satisfaction.
- Understanding User Perceptions of Chatbots: Compilation of preliminary interview questions and answers used to gather user impressions, expectations, and feedback about chatbots and virtual assistants. View Report >
Payment Arrangement Usability Report: Unmoderated testing of how customers use the Virtual Assistant to request payment arrangements. View Report > Power Outage & Account Maintenance Usability Report: Moderated testing of how customers use the Virtual Assistant to report outages and manage account settings. View Report > Service Orders Usability Report: Moderated testing of how customers use the Virtual Assistant to start, stop, or transfer service. View Report > - FAQs Usability Report: Moderated testing of how customers use the Virtual Assistant to handle FAQs like Letter of Residency, Non-Payment power restoration, and Tree Trimming. View Report >
Conceptualize
Tasks:
- Developed User Personas
- Conducted Foundational & Exploratory Research
- Created Sketches and Wireframes
User Personas
Design
Tasks:
- Developed Prototype
- Conducted User Testing
- Build High-Fidelity Designs
Prototype & User Testing
To evaluate the Virtual Assistant’s design and functionality, a combination of testing methods was employed. Moderated and unmoderated usability tests captured real-time feedback on tasks like billing, service orders, and outage reporting, while card sorting validated the platform’s information architecture. Scenario-based tests simulated real-world interactions, and hybrid testing balanced observation with scalability. Feedback sessions provided qualitative insights into user preferences and frustrations, ensuring a comprehensive understanding of user needs.
Customers:
Billing and Payments:
- Findings: Users found bill payment straightforward when using predefined paths, but many expressed a desire for clearer real-time confirmations.
- Opportunity: Adding visual confirmations and summaries improved user confidence in completing payment tasks.
Outage Reporting and Alerts:
- Findings: Real-time updates on outages were highly valued, but users often expected more immediate information within the chatbot rather than being redirected to external pages.
- Opportunity: Enhancing the chatbot’s ability to provide actionable, direct responses for outage-related queries improved user satisfaction and trust.
Account Management:
- Findings: Tasks like resetting passwords and retrieving usernames were common pain points due to unclear prompts or slow processes.
- Opportunity: Simplifying login assistance workflows and providing proactive guidance significantly reduced user frustration.
Stakeholders:
Energy Usage and Efficiency:
- Finding: Users appreciated tools for monitoring energy consumption but wanted more personalized insights tailored to their usage patterns.
- Opportunity: Incorporating actionable energy-saving tips and usage comparisons made the experience more engaging and practical.
Shared Insights Across Features:
- Accessibility Gaps: Users emphasized the need for a unified experience across mobile and desktop platforms.
- Communication Clarity: Clearer prompts, success indicators, and follow-up steps significantly improved task completion rates.
- Scalability Needs: Business users highlighted the importance of managing multiple accounts with minimal manual effort.
Project Outcomes
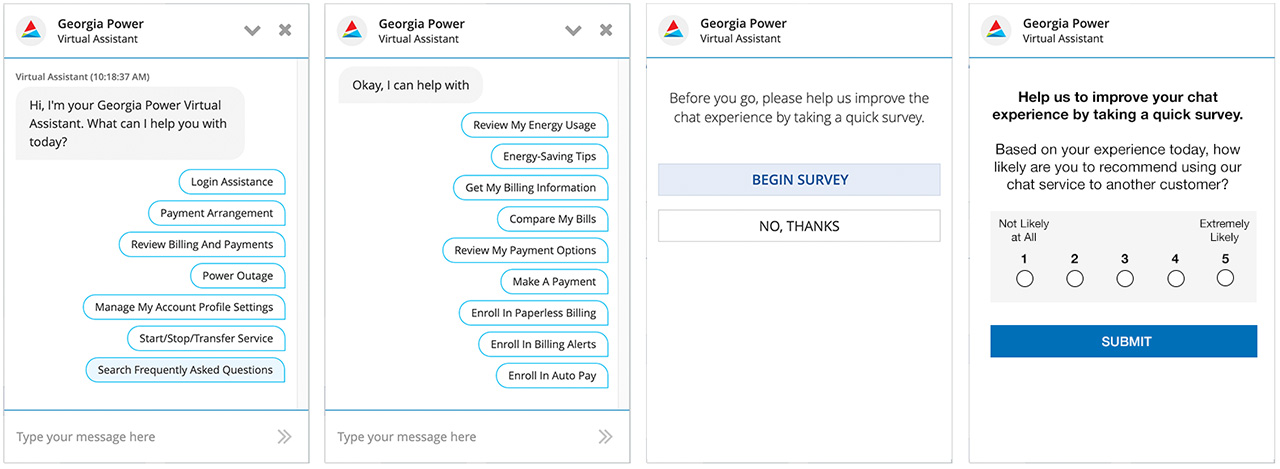
Key performance indicators (KPIs) are based on 3 months of user data collected from company analytics.
Customer Impact:
-
45% Faster Resolutions: Reduced wait times and streamlined workflows allowed customers to complete tasks like bill payments and outage reporting more efficiently.
-
4.7/5 Customer Satisfaction: Users praised the platform for its intuitive design and personalized energy-saving recommendations.
-
59% Increase in Self-Service Adoption: Transitioning users to self-service tools significantly reduced dependence on call centers.
-
62% of Users Valued Real-Time Updates: Access to real-time billing and outage information improved trust and reduced frustration during service disruptions.
-
41% of Customers Acted on Personalized Energy Insights: Tailored recommendations empowered users to make smarter energy choices and save on costs.
Business Impact:
-
23% Reduction in Operational Costs: Automating repetitive tasks decreased the workload on support teams and saved resources.
-
46% Increase in Scalability: The Virtual Assistant efficiently handled a growing number of customer interactions without impacting response times.
-
28% Decrease in Call Center Volume: Self-service adoption significantly reduced the need for live support, freeing up resources for complex issues.
-
62% Retention Rate Among Users: Enhanced satisfaction and trust in the platform contributed to higher customer loyalty.
-
71% of Business Units Leveraged Analytics: Insights from the platform informed continuous improvements and future strategies.
Knowledge Gained
-
Empathy-Driven Design: Understanding customer frustrations with disjointed systems and long wait times emphasized the need for real-time updates and streamlined workflows in similar future projects.
-
Scalability through Automation: Automating repetitive tasks, such as outage reporting and payment processing, showcased how scalable solutions can reduce operational strain and improve service delivery.
-
Data-Informed Iterations: Analytics from user interactions revealed actionable insights, such as prioritizing self-service tools and real-time communication, demonstrating the value of data-driven refinement.
-
Integrated System Challenges: Addressing integration complexities with legacy billing and service systems highlighted the importance of planning for technical constraints in future implementations.
-
Context-Specific Testing: Conducting scenario-based usability tests, such as for outage alerts and account management, reinforced the value of tailoring testing methods to specific use cases for more accurate insights.
Final Designs
Welcome & Customer Feedback Survey
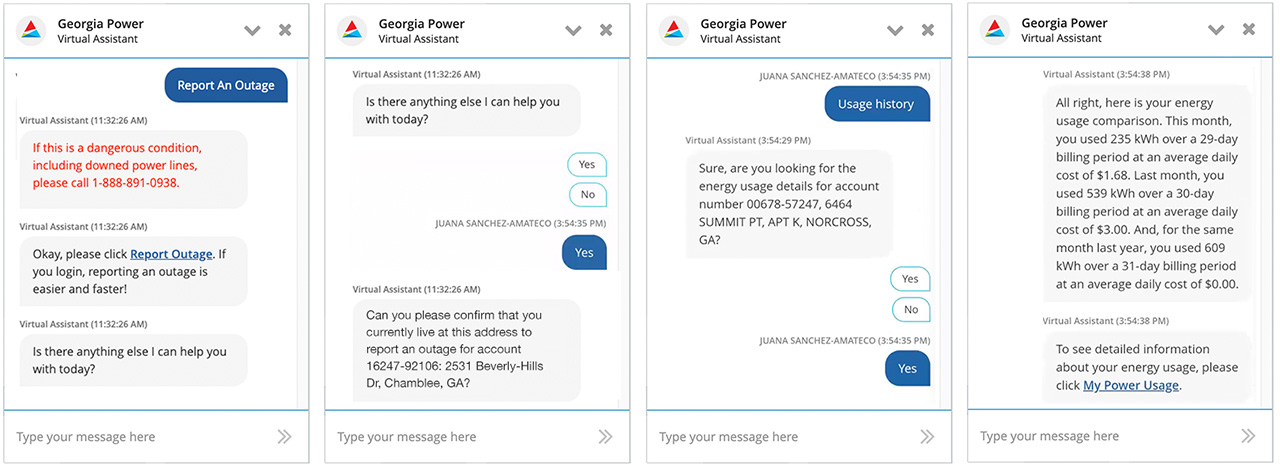
Customer Power Outage & Power Usage
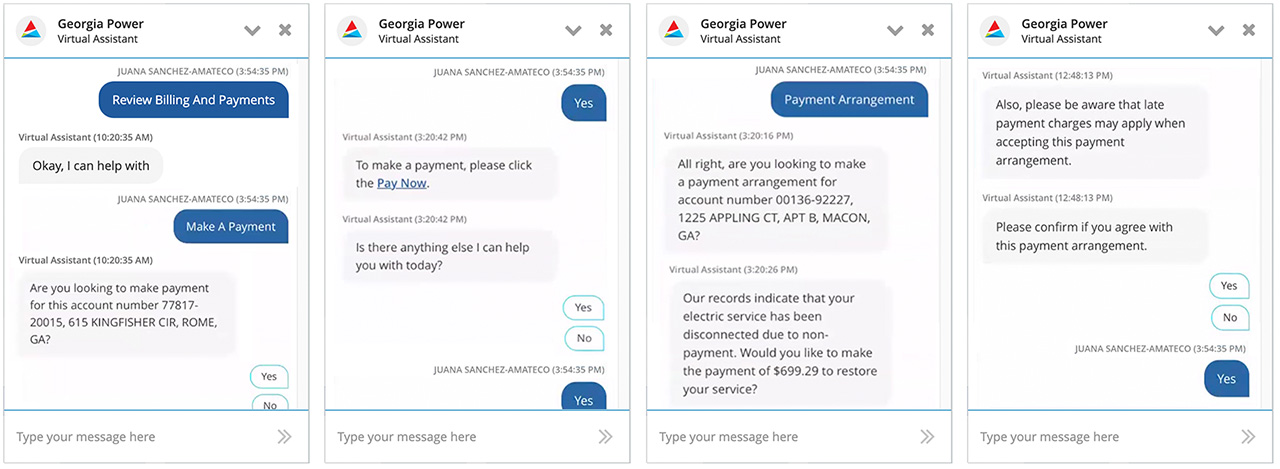
Customer Billing, Payments & Payment Arrangements
Customer Login, Account Profile & Letter of Residency Request